|
MuSTAnG Muon Spaceweather Telescope for Anisotropies Greifswald |

|
|
Welcome to the Homepage of MuSTAnG!The University of Greifswald is developing the MuSTAnG space weather muon telescope which will contribute to the development of European space weather technologies and services. The physics of MuSTAnG
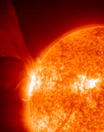
The main activities in space weather come from the Sun and the clouds and particles ejected by the Sun. These clouds and particles can be stormy-like and propagate towards Earth and may endanger human life on Earth as well. MuSTAnG will use very modern technologies to detect particles from space, it will observe cosmic ray muons. Similar technologies are used by large research facilities like the European Nuclear Research Centre CERN nearby Geneva and at DESY (German Electron Synchrotron) Hamburg. MuSTAnG will be able to monitor giant plasma clouds during their propagation between Sun and Earth in real time. Research related to our star – the Sun – will be carried out in Greifswald in two ways: first by means of the fusion reactor Wendelstein 7X at the Max Planck Institute for Plasma Physics and by MuSTAnG at Greifswald University. MuSTAnG in the global networkThe MuSTAnG telescope will be part of a global network of similar muon telescopes, located in Australia, Japan and Brazil. Therefore it will be possible to forecast for the first time precisely and with, until now unachievable, advance warning times of up to 24 hours the arrival time of the plasma clouds at Earth. Tasks of MuSTAnG for daily life
These precise and early warnings of space weather storms allow the potential risks – like interruptions in power supply, positioning errors in satellite navigation, disturbances in telecommunication, radiation exposure of astronauts and other technical effects – to be minimized. For example aircrew members and aircraft electronics are also affected by cosmic rays. MuSTAnG will deliver important data to SWACI (Space Weather Application Center Ionosphere) at German Aerospace Centre DLR Institute for Communication and Navigation Neustrelitz (new federal state Mecklenburg-Vorpommern). MuSTAnG may also support the tourism in the northern regions, because the predictability of polar lights is improved. Who develops and built MuSTAnG?MuSTAnG will be developed and built by the University of Greifswald. At the development and construction of MuSTAnG the following - world wide - institutions will participate: from the new federal states Mecklenburg-Vorpommern and Saxony the University of Applied Sciences Stralsund, the companies 1A Greifswald and HTS Dresden, from Switzerland the University of Bern and from Slovakia the Institute of Experimental Physics Kosice, as well as the University of Shinshu Japan and the Australian Antarctic Division Hobart. This project is supported by the European Space Agency. MuSTAnG is part of the Space Weather European Network - SWENET. The MuSTAnG project at SWENET may be found here. |
last change: June 2007
for questions and comments please contact us here